
Ivana Isgum presents at 2021 SCCT Innovation series
June 9, 2021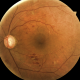
New publication of the Eye Lab in Medical Image Analysis
June 21, 2021
The AI for Oncology Lab establishes a collaboration between the University of Amsterdam (UvA) and the Netherlands Cancer Institute (NKI) with the aim of creating an ecosystem focused on AI technology for Oncology for the improvement of diagnosis and therapy of cancer. The lab counts with Clarisa Sánchez (UvA) and Jan-Jakob Sonke (NKI) as Scientific directors, and Jonas Teuwen (NKI) as Lab manager.
The AI for Oncology Lab is offcially starting, with a kick-off meeting on 24th June 2021. It will be a digital meeting from 16h00 – 17h00. You can register for the opening here. After the registration you will receive a link.
The goal of the collaboration between the Netherlands Cancer Institute (NKI) and University of Amsterdam (UvA) is improved cancer treatment through the aid of Artificial Intelligence. A lot of complex information is acquired from patients during and prior to the treatment through medical imaging, pathology, DNA, and so on. AI solution can assist medical specialists finding and applying the right treatment based on all this information. Moreover, AI algorithms have the potential to guide medical interventions accurately to the location of the tumor without damaging surrounding healthy tissue.
Through this collaboration, expertise in cancer research and AI technology blend together. The first goal is to conduct innovative scientific research. Subsequently, if successful, the lab aims to integrate the results in clinical practice.
The benefits of AI for cancer research
AI technology will play a bigger part in the future of cancer research. Machine learning algorithms can now perform certain tasks that used to require human intelligence. Algorithms based on artificial neural network are used in ‘Deep Learning’. Instead of relying on a programmer to explicitly tell the algorithm what to do, this network only requires an end goal and will learn how to achieve from many examples. The benefits of that is that this ‘Deep Learning’ algorithm can reach insights the programmer would never have considered.
In the case of image recognition for cancer detection, we can use a large database containing images of patients with and without cancer. The computer can use this data to learn and, if the database is sufficiently large, will be able to detect tumors even better than a specialist. In terms of personalized medicine, the images and other data can be used to better predict the most beneficial treatment option for every patient. Image guided therapy aims to deliver therapeutic interventions with high accuracy. AI algorithms can be trained to automatically analyze medical images acquired during treatment and guide the intervention to the correct location.

